Que faisons-nous?
Nous sommes à bord du JCR, le James Clark Ross, un navire de recherche océanographique Britannique, qui doit son nom à un explorateur polaire Anglais.

Le James Clark Ross, a Signy Island. Photo: Bruno Danis
Le but de notre mission est de faire un inventaire, une liste, de tous les animaux qui vivent au fond de la mer (on les appelle les animaux benthiques), dans la région des Orcades du Sud. Ces îles se trouvent entre l’Amérique du Sud et la Péninsule Antarctique, et nous pensons que leur biodiversité doit être protégée. Pour cela, il est important de répertorier tous les animaux qui s’y trouvent (et beaucoup n’ont pas encore été décris), avec comme idée de pouvoir revenir plus tard pour un nouvel inventaire, qui permettra de déceler des changements dûs aux changements de l’environnement.
Comment faisons-nous?
Nous sommes dans une région qui a été relativement peu explorée. La seule manière d’inventorier les animaux qui nous intéresse est de les remonter à la surface. Nous utilisons pour cela des engins semblables à ceux qui sont utilisés par les pêcheurs, mais beaucoup plus petits, pour éviter d’abîmer les fonds. Nous utilisons notamment un AGT (Agassiz Trawl – Chalut Agassiz, du nom de son inventeur) et un traîneau EBS (Epibenthic sledge), qui permet de récolter les animaux qui sont près du fond. Avant de lancer les engins de récolte, nous “scannons” le fond, à l’aide d’un SWATH (qui permet d’avoir une image 3D du fond, très précise), qui fonctionne sur le principe de l’écholocalisation, comme les dauphins ou les chauve-souris… Nous utilisons ensuite une caméra benthique, qui nous permet de prendre de belles photos du fond. Une fois certains que les conditions sont réunies, nous déployons les engins depuis le pont arrière, et déroulons les cables pour atteindre des profondeurs de 500, 750, 1000, 1500 et 2000 m.
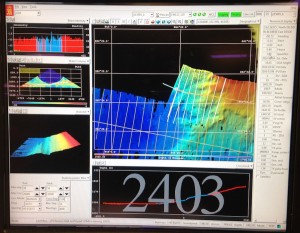
Capture d’ecran du SWATH en action. Les couleurs sont proportionnelles a la profondeur (bleu: plus profond; rouge: moins profond). Photo: Louise Allcock.
Nous remontons ensuite les engins et trions et identifions tous les animaux, ce qui représente un travail très intense, que nous réalisons en équipe.

Lancement du chalut Agassiz depuis le pont arriere du JCR. Photo: Bruno Danis

Une fois a bord, les echantillons sont tries dans le “WetLab”. Photo: Richard Turner
Qu’avons nous trouvé jusqu’ici?
Nous sommes à la moitié de l’expédition, et les différents endroits où nous avons travaillé (que l’on appelle des stations) montrent une diversité très différente. Certaines stations sont relativement pauvres en animaux, mais d’autres sont très riches, et nous avons probablement déjà récolté un nombre important de nouvelles espèces! Ce que nous accumulons comme information devra nous permettre de bien choisir les endroits qui doivent être protégés.
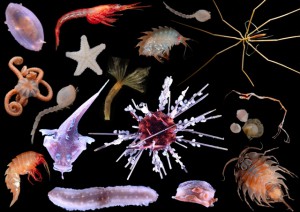
Quelques animaux recoltes au cours de la campagne. Photos: Claudio Ghiglione, Camille Moreau, Helena Wiklund, Cath Waller
Pour en savoir plus… suivez le hashtag #SoAntEco sur Twitter










